UML diagram types
|
|
Class diagram
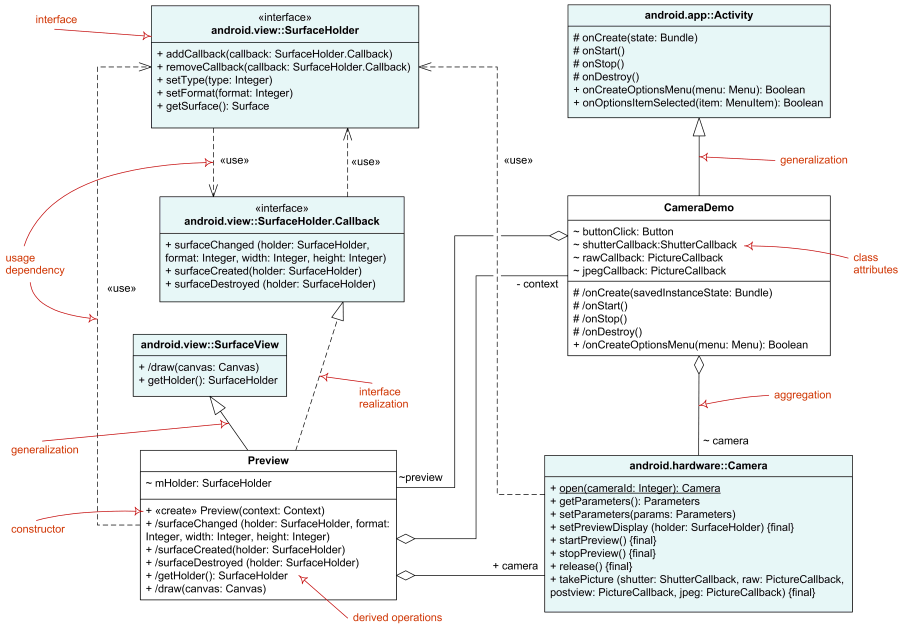
Component diagram
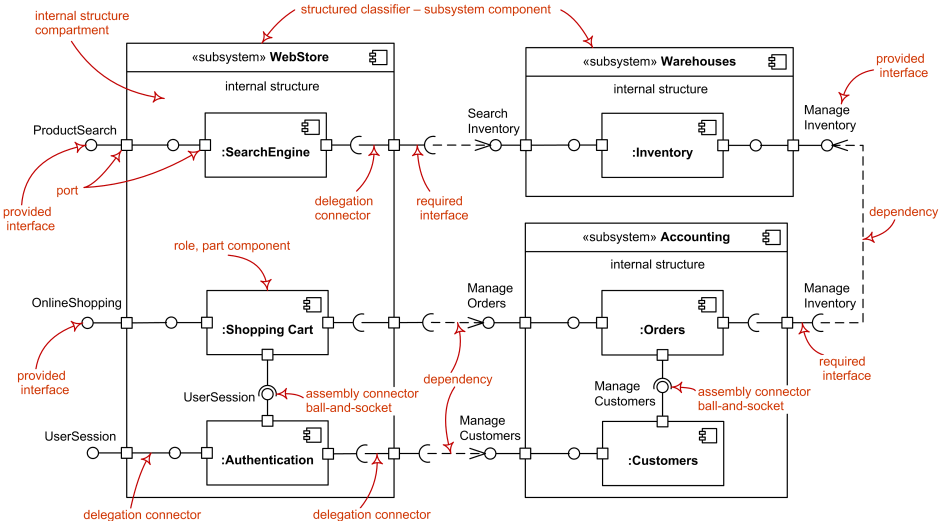
Composite structure diagram

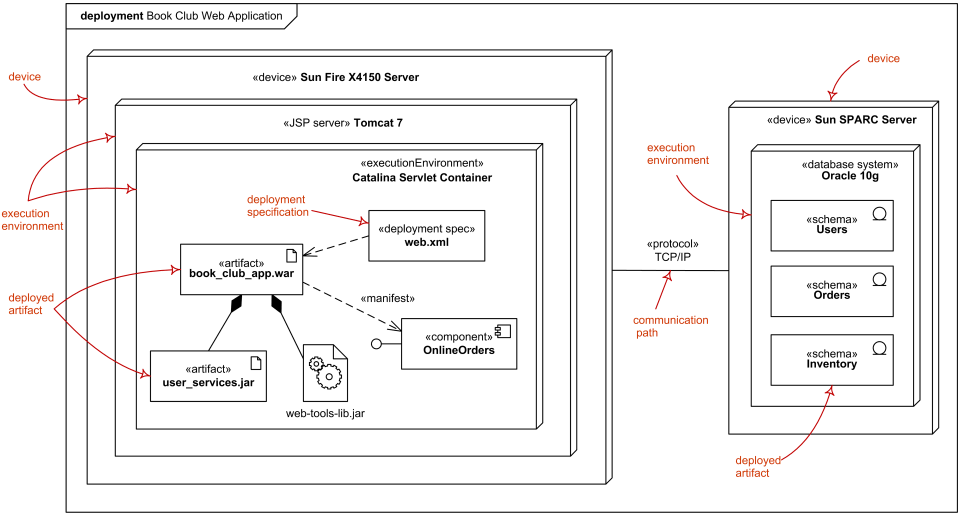
Deployment diagram
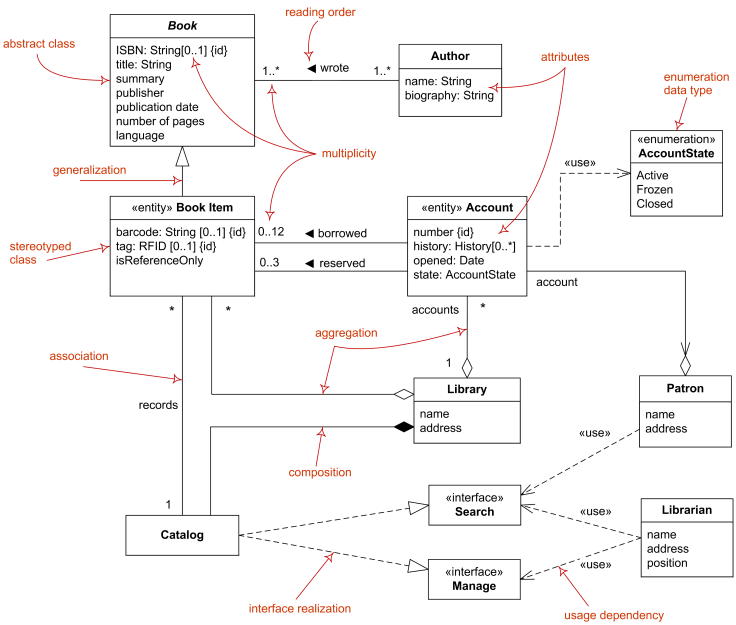
Domain model diagram
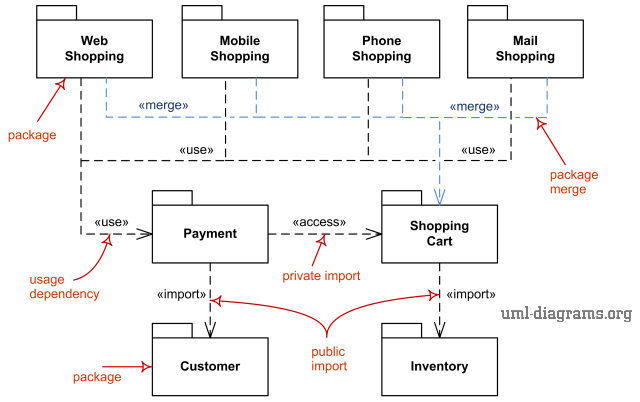
Package diagram
Activity diagram
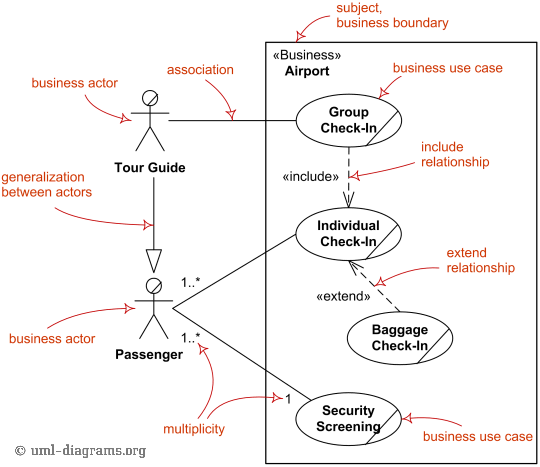
Use case diagram
State diagram
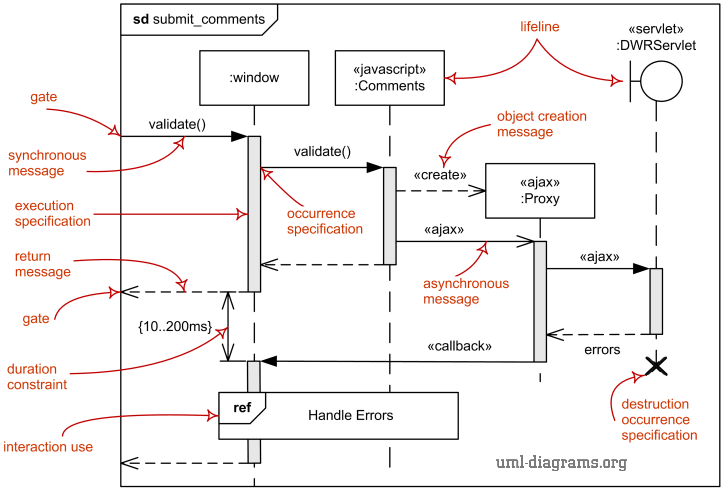
Sequence diagram
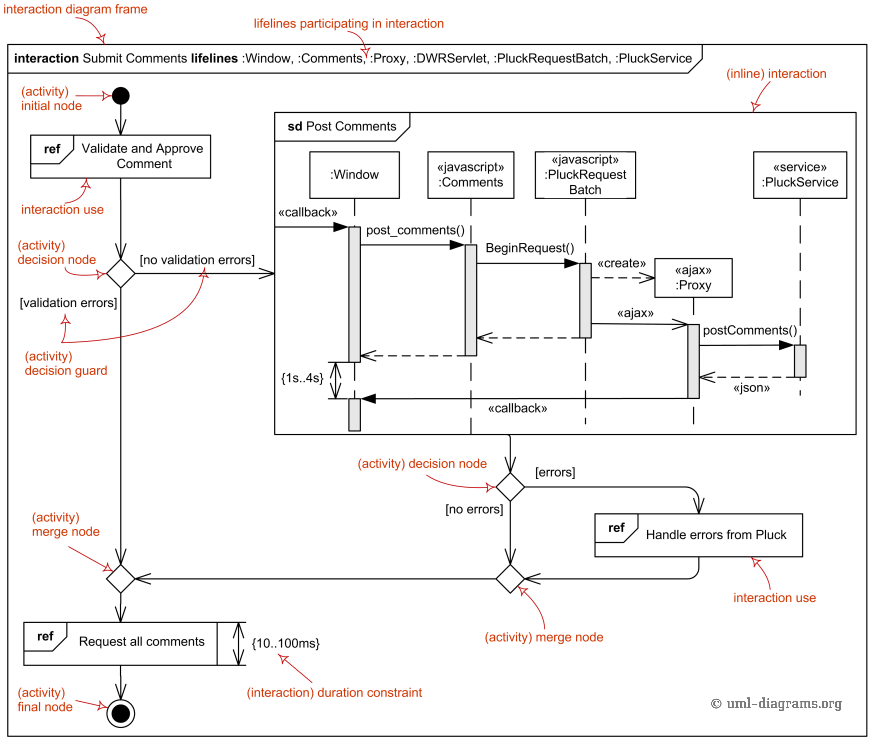
Interaction overview diagram
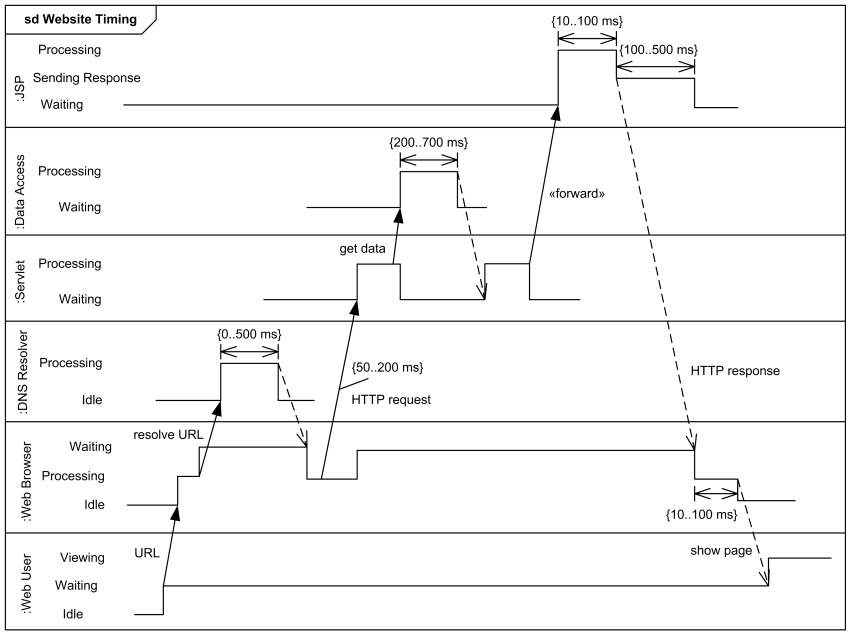
Timing diagram
Fully dressed use case
Alistair Cockburn describes the following fields:
|
|
I have a 4-page example. Want to see it?
Use case diagram

Supplementary Specification
This includes anything specifications not covered in a use case. Possible sections:
|
|